はじめに
今回は、
凸多角形とは
図形に凹みが存在しないとき、
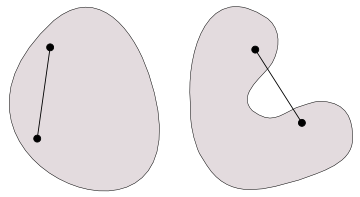
さて、
Blogopolisでは、
今回は、
凸多角形クラスの作成
まず、
public class ConvexPolygon {
private List<Point2D> vertices; // 頂点
private List<LineSegment> edges; // 辺
// verticesには凸多角形の頂点座標が順番に格納してあるものとする
public ConvexPolygon(List<Point2D> vertices) {
int size = vertices.size();
if (size < 3) { // 角数が3未満の場合はエラー
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
this.vertices = vertices;
edges = new ArrayList<LineSegment>();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Point2D v1 = vertices.get(i); // i番目の頂点
Point2D v2 = vertices.get((i + 1) % size); // v1の次の頂点
// 2つの頂点から辺の線分を作成して登録
edges.add(new LineSegment(
v1.getX(), v1.getY(), v2.getX(), v2.getY()));
}
}
// 指定位置の頂点を取得
public Point2D getVertex(int index) {
return vertices.get(index);
}
// 指定位置の辺を取得
public LineSegment getEdge(int index) {
return edges.get(index);
}
// 辺の数(=角数)を取得
public int getEdgeCount() {
return edges.size();
}
}凸性の判定
ConvexPolygonクラスを作成したことで、
多角形の頂点データをもとに、
図4を見てください。多角形の1頂点から出発して、
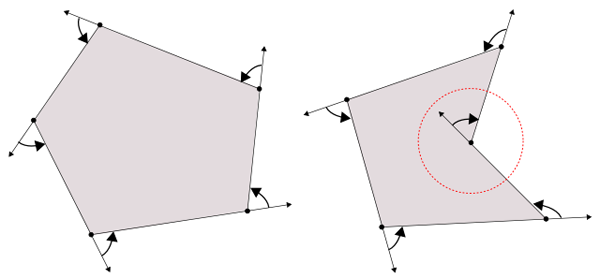
これに対し、
以下、
ベクトルの外積
高校数学で学んだベクトルの内積を憶えているでしょうか。ベクトルaとbの内積
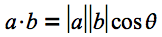
さて、
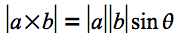
また、
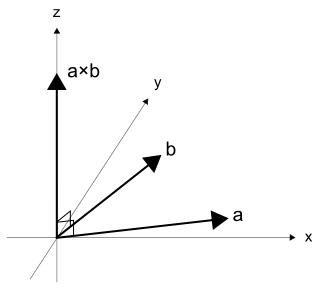
図5を見ると、
外積の計算
平面幾何における外積の式を、
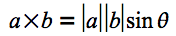
右辺を見ると、
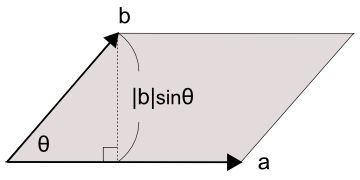
ベクトルaを(x1, y1)、

図7のように補助線を引くと、
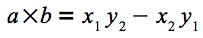
それでは、
public class GeomUtils {
public static double cross(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2) {
return x1 * y2 - x2 * y1;
}
}CCW関数
さて、
入力: 3点a, b, cの座標
出力: a→b→cと進むとき、
なお、
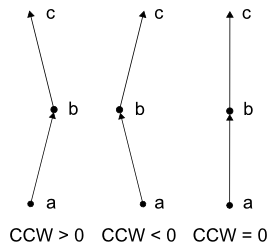
外積とCCW関数には、
では、
public static double ccw(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2,
double x3, double y3) {
return cross(x2 - x1, y2 - y1, x3 - x2, y3 - y2);
}
public static double ccw(Point2D p1, Point2D p2, Point2D p3) {
return ccw(p1.getX(), p1.getY(), p2.getX(), p2.getY(), p3.getX(), p3.getY());
}最後に、
以下、
// verticesには凸多角形の頂点座標が順番に格納してあるものとする
public ConvexPolygon(List<Point2D> vertices) {
int size = vertices.size();
if (size < 3) { // 角数が3未満の場合はエラー
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
this.vertices = vertices;
edges = new ArrayList<LineSegment>();
// 基準となるCCW値を計算
double ccw0 = GeomUtils.ccw(vertices.get(0), vertices.get(1), vertices.get(2));
if (ccw0 == 0) { // ゼロの場合はエラー
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Polygon is not convex.");
}
for (int i = 1; i < size; i++) {
Point2D v1 = vertices.get(i); // i番目の頂点
Point2D v2 = vertices.get((i + 1) % size); // v1の次の頂点
Point2D v3 = vertices.get((i + 2) % size); // v2の次の頂点
double ccw = GeomUtils.ccw(v1, v2, v3); // CCW値を計算
if (ccw0 * ccw <= 0) { // 基準値と符号が異なる、またはゼロの場合はエラー
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Polygon is not convex.");
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Point2D v1 = vertices.get(i); // i番目の頂点
Point2D v2 = vertices.get((i + 1) % size); // v1の次の頂点
// 2つの頂点から辺の線分を作成して登録
edges.add(new LineSegment(
v1.getX(), v1.getY(), v2.getX(), v2.getY()));
}
}まとめと次回予告
今回は、
今回作成したプログラムのソースコードがダウンロードできます。
- 第6回ソースコードファイル
(gihyo-geometry-part6. zip/ Zip圧縮/約95KB)
次回は、



